Table of Contents
The digital heartbeat of modern urban centres
In an era of rapid urbanisation and technological advancement, cities across the globe are embracing digital transformation to address complex challenges and enhance the quality of life for their residents. At the core of this urban evolution lies a powerful tool: the Urban Data Platform. This sophisticated system serves as the digital nervous system of smart cities, collecting, analysing, and utilising vast amounts of information to drive informed decision-making and innovative solutions.
Urban Data Platforms represent a paradigm shift in how municipalities manage their operations and engage with citizens. By integrating diverse data streams from various urban systems, these platforms enable cities to transition from fragmented, reactive approaches to proactive, data-driven strategies. The result is a more efficient, sustainable, and responsive urban environment that can adapt to the ever-changing needs of its inhabitants.
As we delve deeper into the world of Urban Data Platforms, we’ll explore their fundamental components, applications, and the transformative impact they’re having on cities around the world. From improving energy efficiency to reducing traffic congestion, these platforms are reshaping the urban landscape and paving the way for a more connected, intelligent future.
Urbane Datenplattformen und Resilienz der Städte powered by Haselhorst Associates Consulting
Defining the urban data platform
The technological backbone of smart cities
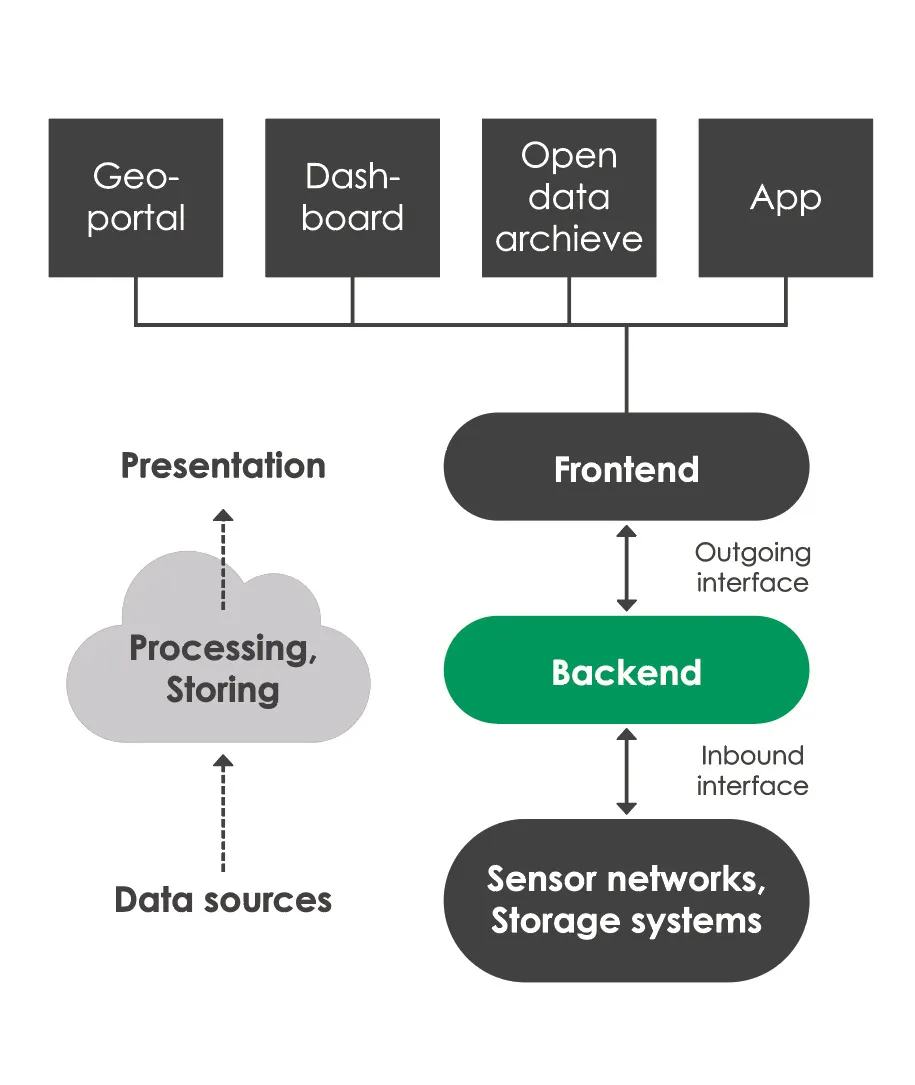
An Urban Data Platform, in its essence, is a comprehensive digital infrastructure that facilitates the collection, integration, and analysis of data from various urban systems and sources. This technological backbone serves as the foundation for developing and implementing smart city initiatives, enabling municipalities to harness the power of information for improved decision-making and service delivery.
At its core, an Urban Data Platform comprises several key components:
- Data Collection Systems: These include sensors, IoT devices, and other data-gathering tools deployed throughout the city.
- Data Storage and Management: Robust databases and cloud storage solutions to securely house the vast amounts of information collected.
- Data Integration Mechanisms: Systems that allow for the seamless combination of data from diverse sources and formats.
- Analytics Engines: Advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities to process and derive insights from the data.
- Visualisation Tools: Interfaces that present data in easily understandable formats for decision-makers and citizens alike.
Open standards and interoperability
A critical aspect of effective Urban Data Platforms is their adherence to open standards and interfaces. This approach, often referred to as an ‘open urban platform’, ensures compatibility and interoperability with other systems and platforms. By adopting open standards, cities can:
- Customise the platform to meet their specific needs and priorities
- Avoid vendor lock-in and reduce long-term technology debt
- Facilitate data sharing with third parties and other stakeholders
- Seamlessly connect various services and data sources
- Provide enhanced digital services to citizens at a lower cost
The adoption of open standards also promotes innovation and collaboration, allowing cities to benefit from a wider ecosystem of solutions and expertise.
The multifaceted applications of urban data platforms
Enhancing municipal operations and services
Urban Data Platforms have a wide range of applications across various aspects of city management and service delivery. Some key areas where these platforms are making a significant impact include:
Transportation and mobility
- Real-time traffic management and congestion reduction
- Optimisation of public transport routes and schedules
- Implementation of smart parking solutions
Energy management
- Monitoring and optimising energy consumption in public buildings
- Integrating renewable energy sources into the urban grid
- Implementing smart street lighting systems
Environmental monitoring
- Air quality measurement and pollution control
- Water management and conservation
- Waste collection and recycling optimisation
Public safety and security
- Crime prediction and prevention through data analysis
- Emergency response coordination
- Disaster preparedness and management
Urban planning and development
- Data-driven land use planning
- Predictive maintenance of infrastructure
- Citizen engagement in urban development projects
Empowering citizens and fostering innovation
Beyond improving municipal operations, Urban Data Platforms play a crucial role in empowering citizens and fostering innovation within the urban ecosystem. By providing access to open data and creating channels for citizen engagement, these platforms enable:
- Development of citizen-centric applications and services
- Increased transparency in government operations and decision-making
- Collaborative problem-solving between citizens, businesses, and local authorities
- Creation of new business opportunities and economic growth
- Enhanced quality of life through personalised services and information
The architecture of urban data platforms
- Data Ingestion Layer:
- Collects data from various sources (IoT devices, legacy systems, external APIs)
- Ensures data quality and standardisation
- Data Storage and Processing Layer:
- Manages both structured and unstructured data
- Implements data governance and security measures
- Analytics and Intelligence Layer:
- Applies advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI algorithms
- Generates insights and predictive models
- Application and Service Layer:
- Hosts various applications and services built on the platform
- Provides APIs for third-party integrations
- Presentation and Visualisation Layer:
- Offers user interfaces for different stakeholders (city officials, citizens, businesses)
- Supports data visualisation and reporting tools
Minimal interoperability mechanisms (MIMs Plus)
To ensure interoperability and facilitate data sharing between different systems and platforms, the concept of Minimal Interoperability Mechanisms (MIMs Plus) has been developed. These mechanisms serve as common building blocks that enable trusted and seamless data flows within the Urban Data Platform ecosystem. Key components of MIMs Plus include:
- Context Information Management: Standardising the way context information is shared
- Shared Data Models: Ensuring consistent interpretation of data across different systems
- Marketplace API: Facilitating the exchange of data and services between stakeholders
- Personal Data Management: Protecting citizens’ privacy and ensuring GDPR compliance
- Fair AI: Promoting ethical and transparent use of artificial intelligence in urban services
By adopting these interoperability mechanisms, cities can create more robust and interconnected Urban Data Platforms that can easily integrate with regional and national digital infrastructures.
Implementing urban data Platforms: Challenges and best practices
Overcoming implementation hurdles
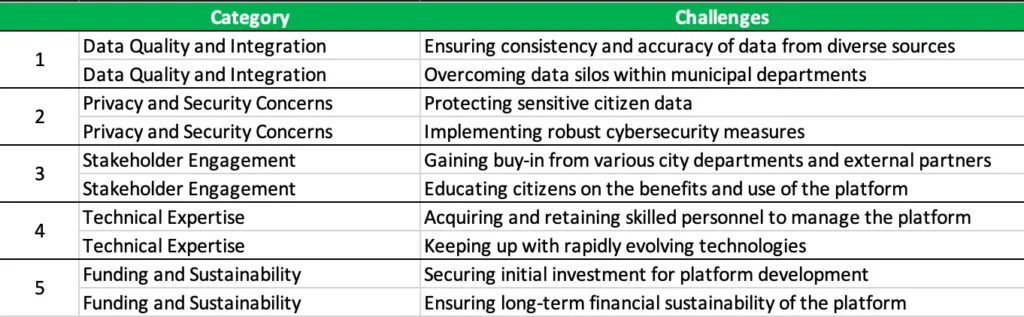
While the benefits of Urban Data Platforms are clear, their implementation comes with a set of challenges that cities must navigate:
Best practices for successful implementation
To address the challenges and maximize the benefits of Urban Data Platforms, cities can adopt several best practices for successful implementation. First, they should develop a clear data strategy, defining specific use cases and objectives for the platform, and establishing data governance policies and standards. Adopting a phased approach is also crucial, starting with pilot projects to demonstrate value and gradually scaling up based on insights gained. Collaboration plays a key role in success, involving partnerships with academia, industry, and other cities, as well as actively engaging citizens in the design and implementation process.
Investing in capacity building is essential, providing training and upskilling opportunities for city staff, while cultivating a data-driven culture within the organization. Additionally, ensuring transparency and trust is critical, with clear communication on data usage and privacy measures, and the implementation of ethical guidelines for data handling and AI applications. Finally, cities should leverage existing resources by utilizing open-source solutions and shared platforms wherever possible, and drawing on best practices and case studies from other cities.
By following these best practices, cities can overcome common hurdles and create robust, effective Urban Data Platforms that drive meaningful change within their communities.
The economic impact of urban data platforms
Driving innovation and economic growth
Urban Data Platforms have the potential to catalyse significant economic growth and innovation within cities. By providing a rich ecosystem of data and services, these platforms create new opportunities for businesses, entrepreneurs, and researchers. Some of the key economic benefits include:
- Stimulating the Digital Economy:
- Encouraging the development of new digital services and applications
- Supporting the growth of local tech startups and SMEs
- Improving Resource Allocation:
- Enabling data-driven decision-making for more efficient use of city resources
- Reducing operational costs through predictive maintenance and optimisation
- Attracting Investment:
- Positioning the city as a hub for innovation and smart technologies
- Encouraging private sector investment in urban development projects
- Creating New Job Opportunities:
- Generating demand for data scientists, software developers, and other tech professionals
- Fostering the development of new skills and competencies in the workforce
Quantifying the value of urban data platforms
While the benefits of Urban Data Platforms are clear, quantifying their economic impact can be challenging. However, several studies and case examples demonstrate their potential value:
- A study by McKinsey Global Institute estimated that smart city technologies could create an economic value of $2.3 trillion globally by 2025.
- The city of Barcelona reported annual savings of €75 million through smart water management and €50 million through smart lighting initiatives powered by their Urban Data Platform.
- In Helsinki, the open data initiative facilitated by their Urban Data Platform has led to the creation of over 100 new companies and 1,500 jobs.
To fully realise these economic benefits, cities must focus on:
- Developing sustainable business models for their Urban Data Platforms
- Creating incentives for businesses to utilise and contribute to the platform
- Measuring and communicating the economic impact of platform-driven initiatives
- Fostering a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship within the urban ecosystem
The future of urban data platforms
Emerging trends and technologies
As Urban Data Platforms continue to evolve, several emerging trends and technologies are shaping their future development:
- Advanced predictive analytics for urban planning and management
- Automated decision-making systems for real-time city operations
- Creating virtual replicas of cities for simulation and scenario planning
- Integrating real-time data for dynamic urban modelling
- Enabling faster, more reliable data collection and processing
- Supporting real-time applications and services at the edge
- Enhancing data security and transparency
- Facilitating secure data sharing and transactions between stakeholders
- Improving urban planning and citizen engagement through immersive experiences
- Enhancing maintenance and operations through AR-assisted workflows
The road ahead: Challenges and opportunities
As cities explore the future of Urban Data Platforms, they face a landscape marked by both significant challenges and promising opportunities. One major consideration is data ethics and governance, which involves developing frameworks for responsible AI and data usage. Cities must balance the drive for innovation with the need to protect privacy and uphold ethical standards. Another priority is interoperability and standardisation, where promoting global standards can enhance the compatibility of Urban Data Platforms and facilitate data sharing and collaboration across cities and regions.
Resilience and sustainability are also central, as Urban Data Platforms offer valuable tools to tackle climate change and environmental issues, while bolstering urban resilience through data-driven disaster preparedness and response strategies. To achieve digital inclusion, cities must ensure equitable access to digital services, working to bridge the digital divide within urban populations.
A citizen-centric design approach is essential as well, involving residents in co-creating urban solutions and building platforms that genuinely reflect the needs and aspirations of their communities.
By proactively addressing these challenges and leveraging emerging opportunities, cities can develop Urban Data Platforms that go beyond solving today’s issues, laying a strong foundation for smart, sustainable, and inclusive urban centers of the future.
Embracing the urban data revolution
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in urban development, Urban Data Platforms emerge as a transformative force, reshaping the way cities operate, innovate, and engage with their citizens. These sophisticated digital ecosystems offer unprecedented opportunities to address urban challenges, from traffic congestion and energy efficiency to public safety and environmental sustainability.
The journey towards fully realising the potential of Urban Data Platforms is not without its challenges. Cities must navigate complex issues of data privacy, interoperability, and sustainable funding. However, the potential rewards – in terms of improved quality of life, economic growth, and environmental stewardship – far outweigh these obstacles. As we look to the future, it is clear that Urban Data Platforms will play an increasingly central role in shaping the smart cities of tomorrow. By embracing open standards, fostering collaboration, and putting citizens at the heart of their design, these platforms can help create urban environments that are not just smarter, but also more inclusive, resilient, and sustainable. The urban data revolution is here, and it offers a powerful toolkit for cities to reimagine their future. As more municipalities around the world adopt and refine these platforms, we can look forward to a new era of urban innovation, where data-driven insights lead to tangible improvements in the lives of millions of city dwellers worldwide.
Literature
- Urban data platforms: https://www.iese.fraunhofer.de/en/trend/smart-city/urban-data-platform.html
- Cities are becoming digital – Urban Data Platforms enable it: https://smart-cities-marketplace.ec.europa.eu/news-and-events/news/2020/cities-are-becoming-digital-urban-data-platforms-enable-it
- Urbane Datenplattformen: Das Herzstück der Smart City: https://www.smart-city-dialog.de/informieren/aktuelles/urbane-datenplattformen-das-herzstueck-der-smart-city
- Smart cities: Digital solutions for a more livable future: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/operations/our-insights/smart-cities-digital-solutions-for-a-more-livable-future




