The low-carbon production
As the world grapples with the pressing issue of climate change, the concept of low-carbon production has emerged as a crucial solution to mitigate the detrimental impacts of greenhouse gas emissions. In this era of environmental consciousness, it is imperative for you to comprehend the significance of transitioning to sustainable manufacturing practices that prioritize the reduction of carbon footprints.
Low-carbon production encompasses a wide range of strategies and technologies aimed at minimizing the emission of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases during the manufacturing process. By adopting these eco-friendly approaches, industries can contribute to the global effort of combating climate change while simultaneously fostering economic growth and environmental stewardship.
The pursuit of low-carbon production is not merely a fleeting trend; it is a fundamental necessity for safeguarding the planet's future. As you delve deeper into this topic, you will gain invaluable insights into the intricate web of factors that influence the transition towards a greener and more sustainable industrial landscape.
The importance of reducing carbon emissions
The urgency to reduce carbon emissions cannot be overstated. The consequences of inaction are severe and far-reaching, affecting not only the environment but also the well-being of future generations. By embracing low-carbon production methods, you have the power to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Excessive carbon emissions are the primary driver of global warming, leading to rising temperatures, sea level rise, and an increased frequency of extreme weather events. These environmental disruptions have profound implications for ecosystems, biodiversity, food security, and human health. By transitioning to low-carbon production, you can play a pivotal role in addressing these pressing challenges.
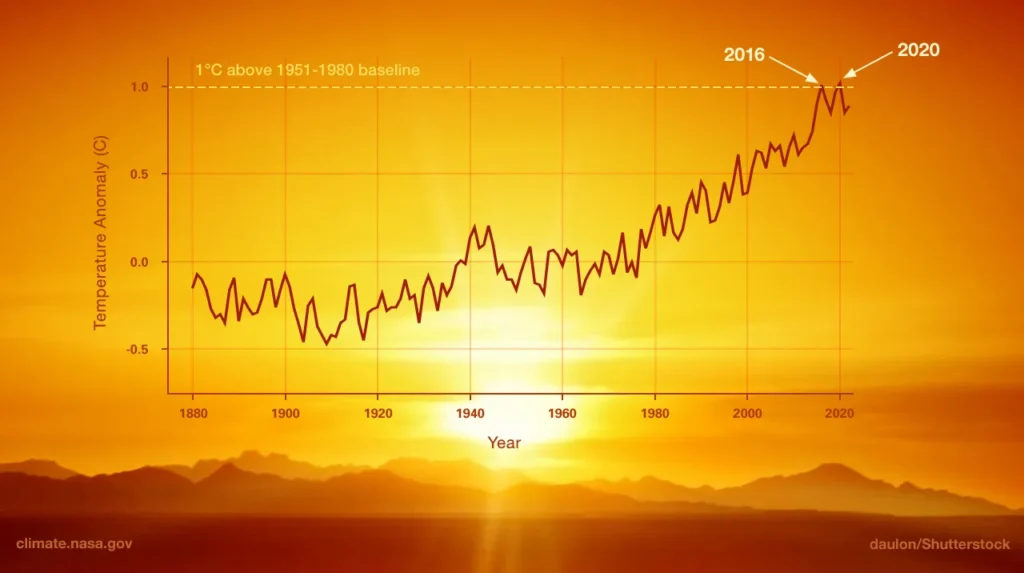
This graph illustrates the change in global surface temperature relative to 1951-1980 average temperatures, with the year 2020 statistically tying with 2016 for hottest on record (Source: NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies). Learn more about global surface temperature here. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech. Image credit: true
Moreover, the economic benefits of reducing carbon emissions are substantial. As governments and consumers become increasingly environmentally conscious, industries that prioritize sustainability will gain a competitive advantage in the market. By embracing low-carbon production, you can position your business for long-term success while simultaneously contributing to a healthier planet.
Key drivers of climate catastrophe
To effectively address the low-carbon production puzzle, it is crucial to understand the key drivers of climate catastrophe. These factors have a profound impact on the Earth's delicate ecosystem and serve as catalysts for the urgent need to transition towards sustainable practices.
- Fossil Fuel Combustion: The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, for energy production and transportation is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. These non-renewable resources release vast amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, exacerbating the greenhouse effect and accelerating climate change.
- Deforestation and Land-Use Changes: The clearing of forests and conversion of land for agricultural or urban development not only destroys vital carbon sinks but also releases stored carbon into the atmosphere. Deforestation and unsustainable land-use practices disrupt the delicate balance of the Earth's carbon cycle, compounding the effects of climate change.
- Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes, such as cement production, chemical manufacturing, and metal smelting, generate significant amounts of greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions contribute to the overall carbon footprint of industries and exacerbate the challenges associated with climate change.
- Agricultural Practices: Certain agricultural practices, such as the use of synthetic fertilizers, livestock farming, and rice cultivation, release potent greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide. These emissions, combined with the energy-intensive nature of modern agriculture, contribute significantly to the overall carbon footprint of the food production system.
By understanding and addressing these key drivers, you can take proactive steps towards implementing low-carbon production strategies and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Understanding the low-carbon production puzzle
Unraveling the low-carbon production puzzle requires a holistic approach that considers the intricate interplay of various factors. It is a multifaceted challenge that demands innovative solutions and a commitment to sustainable practices across all sectors of the economy.
At the core of this puzzle lies the need to decouple economic growth from carbon emissions. Traditional manufacturing processes have long been associated with high levels of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing significantly to the global carbon footprint. However, the transition to low-carbon production offers a pathway to reconcile economic development with environmental sustainability.
To navigate this puzzle successfully, you must embrace a multidisciplinary approach that incorporates technological advancements, policy reforms, behavioral changes, and collaborative efforts among stakeholders. By understanding the interconnected nature of the low-carbon production puzzle, you can develop comprehensive strategies that address the root causes of climate change while fostering economic prosperity.
The role of renewable energy in reducing carbon footprint
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is a pivotal component of the low-carbon production puzzle. By harnessing the power of clean and sustainable energy sources, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint while ensuring a reliable and cost-effective energy supply.
Capturing the abundant energy from the sun through photovoltaic (PV) systems and concentrated solar power (CSP) technologies offers a clean and renewable source of electricity. As solar technology continues to advance and become more affordable, it presents a viable alternative to fossil fuel-based energy generation.
Harnessing the power of wind through wind turbines is another promising renewable energy source. With increasing efficiency and decreasing costs, wind energy has the potential to play a significant role in meeting the energy demands of industries while minimizing carbon emissions.
Utilizing the kinetic energy of flowing water to generate electricity through hydroelectric power plants is a well-established and efficient form of renewable energy. While large-scale hydropower projects can have environmental impacts, small-scale and run-of-river hydropower systems offer a sustainable solution for industrial energy needs.
Data-Driven Sustainability: Leveraging Analytics for Urban Resilience
Read More →Tapping into the Earth's internal heat through geothermal power plants provides a consistent and reliable source of renewable energy. This technology has the potential to contribute significantly to the energy mix, particularly in regions with high geothermal activity.
By embracing these renewable energy sources and integrating them into your industrial processes, you can significantly reduce your reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to the global effort of mitigating climate change.
The role of industries in transitioning to low-carbon production
Industries play a crucial role in the transition towards low-carbon production. As major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, it is imperative for businesses to adopt sustainable practices and prioritize the reduction of their carbon footprint.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient technologies and optimizing industrial processes can significantly reduce energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. This can be achieved through measures such as upgrading equipment, improving insulation, and implementing energy management systems.
- Material Efficiency: Maximizing the efficient use of raw materials and minimizing waste can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of industrial processes. This can be accomplished through strategies such as lean manufacturing, recycling, and closed-loop systems.
- Green Supply Chain Management: Adopting sustainable practices throughout the supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to distribution and logistics, can contribute to reducing the overall carbon footprint of industrial operations. This involves collaborating with suppliers, optimizing transportation routes, and implementing sustainable packaging solutions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): While still in the developmental stages, CCS technologies offer the potential to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes, preventing them from being released into the atmosphere. As these technologies mature, they could play a significant role in mitigating the carbon footprint of industries.
By embracing these strategies and actively participating in the transition towards low-carbon production, industries can not only contribute to the fight against climate change but also position themselves as leaders in sustainable business practices.
Government policies and regulations for low-carbon production
Governments play a pivotal role in facilitating and incentivizing the transition to low-carbon production through the implementation of effective policies and regulations. These measures can create a conducive environment for businesses to adopt sustainable practices while addressing the challenges posed by climate change.
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms: Implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or emissions trading schemes, can incentivize industries to reduce their carbon footprint by internalizing the environmental costs associated with greenhouse gas emissions.
- Renewable Energy Incentives: Providing financial incentives, such as tax credits, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs, can encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources and accelerate the transition towards low-carbon production.
- Emissions Regulations: Establishing stringent emissions regulations and standards can drive industries to adopt cleaner technologies and implement sustainable practices to comply with environmental regulations.
- Research and Development Funding: Investing in research and development initiatives focused on low-carbon technologies, energy efficiency, and sustainable manufacturing processes can foster innovation and accelerate the transition towards a low-carbon economy.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Fostering collaboration between government agencies, industries, and research institutions through public-private partnerships can facilitate knowledge sharing, resource allocation, and the development of innovative solutions for low-carbon production.
By implementing these policies and regulations, governments can create an enabling environment that supports and incentivizes industries to embrace low-carbon production practices, ultimately contributing to the global effort of mitigating climate change.
Innovations and technologies for sustainable production
Technological innovations play a pivotal role in enabling the transition towards low-carbon production. By embracing cutting-edge technologies and fostering a culture of innovation, you can unlock new possibilities for sustainable manufacturing practices and reduce your carbon footprint.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): The integration of connected devices, sensors, and data analytics in industrial processes can optimize resource utilization, improve energy efficiency, and reduce waste. IIoT technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and intelligent decision-making, leading to a more sustainable and efficient production environment.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, offers a more sustainable approach to production by reducing material waste, enabling on-demand manufacturing, and minimizing transportation costs. This technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chains and manufacturing processes, leading to a significant reduction in carbon emissions.
- Biotechnology and Biomanufacturing: Leveraging the power of biotechnology and biomanufacturing can provide sustainable alternatives to traditional manufacturing processes. From bioplastics to biofuels and bioremediation, these technologies offer innovative solutions for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a circular economy.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms in industrial processes can optimize resource allocation, predict maintenance needs, and identify opportunities for energy savings. These technologies can help industries achieve higher levels of efficiency and sustainability while reducing their carbon footprint.
- Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies: The use of hydrogen as an energy carrier and the development of fuel cell technologies offer promising solutions for low-carbon energy generation and storage. As these technologies mature, they could play a significant role in decarbonizing industrial processes and transportation systems.
By embracing these innovations and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, you can position your business as a leader in sustainable production practices, contributing to the global effort of mitigating climate change while maintaining a competitive edge.
Taking action for a low-carbon future
The transition towards low-carbon production is not merely a choice; it is an imperative for safeguarding the planet's future and ensuring the well-being of generations to come. By understanding the key drivers of climate catastrophe and embracing sustainable practices, you have the power to contribute to a more sustainable and resilient world.
The low-carbon production puzzle may seem daunting, but it is a challenge that can be overcome through collective action, innovative thinking, and a commitment to environmental stewardship. By harnessing the power of renewable energy, implementing energy-efficient technologies, and fostering a culture of sustainability within your organization, you can pave the way for a low-carbon future.
Remember, the journey towards a sustainable tomorrow begins with the actions you take today. Embrace the principles of low-carbon production, collaborate with stakeholders, and advocate for policies that support a greener and more resilient economy. Together, we can unlock the potential of sustainable manufacturing practices and create a legacy of environmental responsibility for future generations.Join the movement towards a low-carbon future by taking action today. Start by conducting an energy audit of your industrial processes and identifying areas for improvement. Explore the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, into your operations. Engage with your employees, suppliers, and stakeholders to foster a culture of sustainability and implement best practices for reducing your carbon footprint. Remember, every step you take towards low-carbon production contributes to a brighter and more sustainable future for all.
Literature
- Understanding and responding to danger from climate change: the role of key risks in the IPCC AR5: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10584-016-1645-x
- Human and Natural Drivers of Climate Change (1850-2018): https://science.nasa.gov/resource/human-and-natural-drivers-of-climate-change-1850-2018/
- What Is Climate Change?: https://climate.nasa.gov/what-is-climate-change.amp
- Understanding the Causes of Climatic Change in the Environment: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-86290-9_3


