Table of Contents
The data-driven sustainability
In today’s fast-paced world, sustainability isn’t just a buzzword – it’s a necessity. With cities facing the pressures of rapid growth, dwindling resources, and climate challenges, a smarter way forward is essential. That’s where data-driven sustainability steps in. By tapping into the power of data, we can make sharper decisions, use resources more wisely, and shape cities that thrive for generations to come.
Think of it as turning information into action. With the right insights, cities can measure progress, adapt to changing needs, and stay ahead of the curve. Embracing this approach gives us the tools to tackle the complexities of urban life while protecting the planet and improving the lives of the people who call it home. The future isn’t just about surviving – it’s about thriving, and data can help us get there.
Understanding the concept of urban resilience
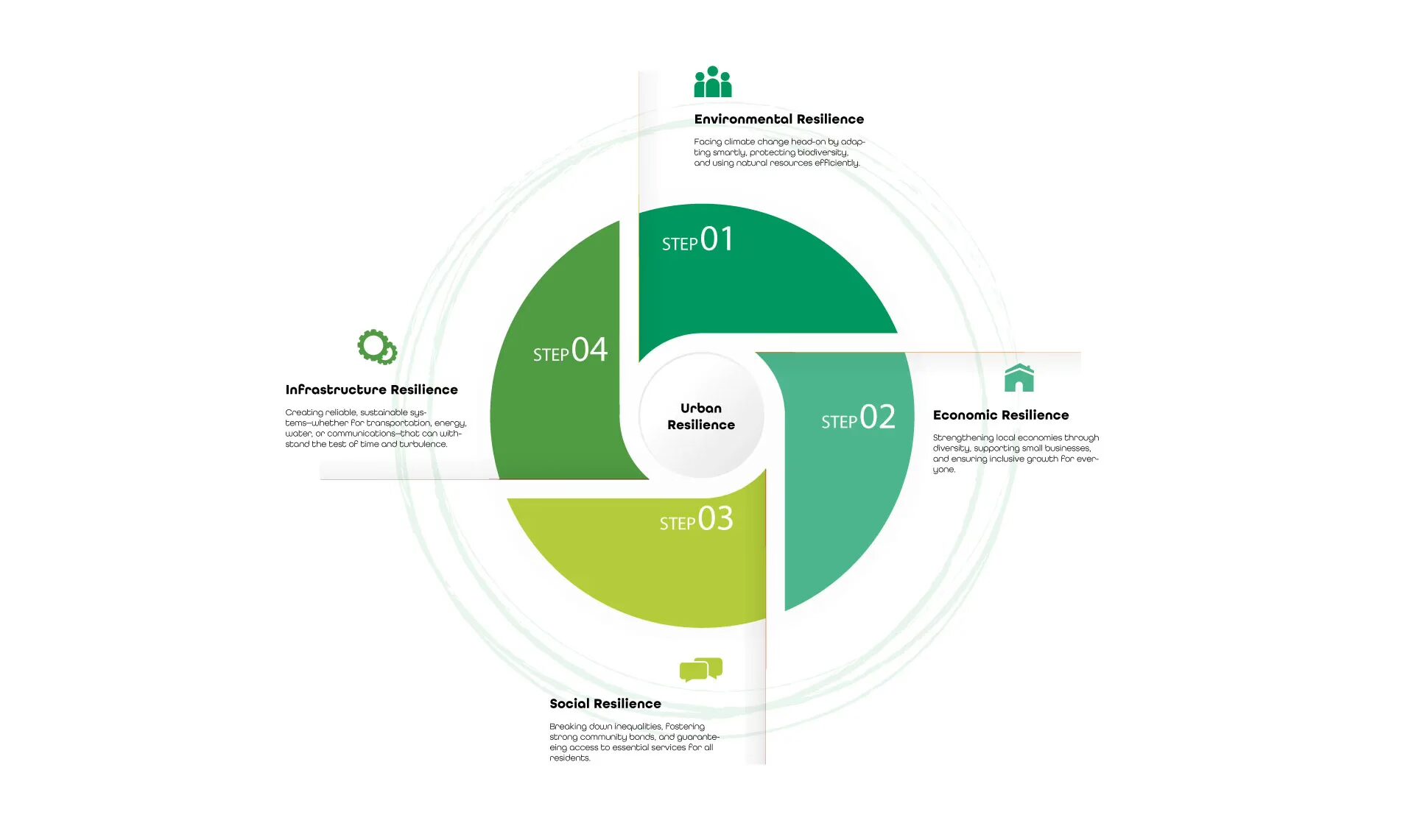
Urban resilience is all about helping cities not just survive challenges but thrive despite them. It’s the ability to bounce back from disruptions – be they environmental, economic, or social – while keeping essential services running and communities intact. But building a resilient city takes more than quick fixes; it demands a well-rounded, sustainable approach that tackles multiple fronts:
- Environmental Resilience: Facing climate change head-on by adapting smartly, protecting biodiversity, and using natural resources efficiently.
- Economic Resilience: Strengthening local economies through diversity, supporting small businesses, and ensuring inclusive growth for everyone.
- Social Resilience: Breaking down inequalities, fostering strong community bonds, and guaranteeing access to essential services for all residents.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Creating reliable, sustainable systems—whether for transportation, energy, water, or communications – that can withstand the test of time and turbulence.
When cities embrace resilience, they’re better equipped to handle shocks and stresses while laying the groundwork for a future that’s not only sustainable but prosperous for generations to come.
Concept of urban resilience – greenfriendlylabs.com
The role of analytics in sustainable urban development
Analytics transforms data into actionable insights, helping cities tackle challenges and seize opportunities. By guiding smarter decisions, it lays the foundation for sustainable, resilient urban development.
- Resource Management: Analytics can help optimize resource utilization, such as energy, water, and waste management, by identifying inefficiencies and implementing targeted interventions.
- Urban Planning: Geospatial data and predictive modeling can inform urban planning decisions, enabling cities to design sustainable infrastructure, optimize land use, and anticipate future growth patterns.
- Climate Resilience: By analyzing historical climate data and modeling future scenarios, cities can develop effective mitigation and adaptation strategies to address the impacts of climate change.
- Citizen Engagement: Data-driven platforms can facilitate citizen engagement, enabling residents to provide feedback, report issues, and participate in decision-making processes related to sustainable development.
By leveraging analytics, cities can transition from reactive to proactive approaches, anticipating challenges, and implementing sustainable solutions that foster long-term resilience.
Benefits of data-driven sustainability
Adopting a data-driven approach to sustainability unlocks a host of benefits for both urban communities and the environment. Here’s what makes it a game-changer:
- Smarter Decision-Making: By grounding policies and initiatives in solid data, cities can make informed, context-specific choices that address real needs effectively.
- Optimized Resource Use: Data analysis reveals patterns in resource consumption, helping cities reduce waste, improve efficiency, and promote sustainability.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracking air quality, emissions, water health, and biodiversity allows cities to identify issues early and take proactive measures to mitigate environmental impacts.
- Citizen Engagement and Transparency: Open access to data encourages residents to get involved in sustainability efforts, fostering accountability and stronger community participation.
- Cost Savings: Efficiency and targeted interventions reduce expenses, freeing up resources for investing in infrastructure, green initiatives, and community development.
By embracing data-driven sustainability, cities can unlock a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement, where data-driven insights inform evidence-based decision-making, leading to more sustainable and resilient urban environments.
Case studies on successful implementation of data-driven sustainability
Cities around the world have recognized the potential of data-driven sustainability and have implemented innovative solutions to address urban challenges. Here are some inspiring case studies:
The city has implemented a comprehensive data-driven approach to urban planning and management. Sensors and data analytics are used to optimize energy consumption, improve waste management, and enhance mobility solutions. Barcelona’s “City OS” platform integrates data from various sources, enabling real-time monitoring and decision-making.

Barcelona: Pioneering the evolution of smart urban environments
Known for its commitment to sustainability, Copenhagen has leveraged data analytics to achieve its ambitious climate goals. The city’s “Copenhagen Solutions” initiative utilizes data to optimize energy consumption in buildings, promote sustainable transportation, and enhance urban resilience.

This city-state has embraced data-driven solutions to address challenges related to urban density, resource scarcity, and climate change. The “Virtual Singapore” project is a comprehensive digital twin of the city, enabling urban planners to simulate and test various scenarios before implementation.

The city has implemented the “NYC Open Data” initiative, providing public access to over 2,000 datasets related to various urban domains, including sustainability, transportation, and public safety. This data-driven approach has enabled the development of innovative solutions and fostered citizen engagement.

These case studies demonstrate the transformative power of data-driven sustainability, showcasing how cities can leverage data analytics to drive sustainable urban development, enhance resilience, and create livable and thriving communities.
Key principles for leveraging analytics for urban resilience
To really make the most of analytics for urban resilience, cities need to follow some guiding principles that help ensure their data-driven initiatives are effective and sustainable. First off, data governance is crucial – this means setting up strong frameworks to keep data secure, private, and ethically used. Clear policies should guide how data is collected and managed.
Next, stakeholder engagement is key. Involving a mix of people – like citizens, community groups, businesses, and government agencies – in the planning and execution of sustainability projects builds trust and leads to solutions that fit local needs.
Then there’s capacity building. Investing in training and resources helps everyone involved develop the technical skills needed to use data effectively for making sustainable decisions.
Another important principle is interoperability and integration. By ensuring that data systems across different urban areas – like transportation, energy, and waste management – can work together, cities can take a more holistic approach to resilience.
It’s also vital to embrace continuous improvement. This means regularly checking how well initiatives are working and being ready to adapt based on feedback and new data.
Finally, transparency and accountability are essential. Cities should be open about how they collect and analyze data, allowing citizens to provide input and hold decision-makers accountable.
By sticking to these principles, cities can build a strong foundation for using analytics to enhance urban resilience, paving the way for sustainable and inclusive development while tackling the complex challenges of our time.
Tools and technologies for data collection and analysis in sustainable development
Internet of Things (IoT) and Sensor Networks
IoT devices and sensor networks enable the collection of real-time data on various urban parameters such as air quality, traffic patterns, energy consumption and waste management. These data streams provide valuable insights for optimising resource use and identifying areas for improvement.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS technologies enable the integration and analysis of spatial data, facilitating urban planning, land use optimisation and environmental monitoring. GIS tools can be used to visualise and analyse data related to transport networks, green spaces and infrastructure development.
Big Data Analytics
Advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and predictive modelling, can be applied to large data sets to uncover patterns, trends and insights that inform sustainable decision-making. These techniques can be used to predict resource demand, optimise energy consumption and identify potential environmental risks.
Data Visualization and Dashboards
Effective data visualisation and dashboard tools are essential for communicating complex data in a clear and accessible way. These tools enable stakeholders, including policymakers and citizens, to understand and engage with data-driven insights, promoting transparency and informed decision-making.
Cloud Computing and Data Storage
Cloud-based solutions provide scalable and secure data storage and computing resources, enabling cities to efficiently manage and analyse large volumes of data. Cloud technologies also facilitate data sharing and collaboration between different stakeholders.
Open Data Platforms
Developing open data platforms that provide public access to urban data can promote transparency, citizen engagement, and the development of innovative solutions by third-party developers and researchers. By using these tools and technologies, cities can unlock the full potential of data-driven sustainability, enabling informed decision-making, optimising resource use and promoting urban resilience in the face of complex challenges.
Steps to develop a data-driven sustainability plan
1. Define sustainability goals and objectives
Clearly define your city’s sustainability goals and objectives, aligning them with international frameworks such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and local priorities.

2. Conduct a baseline assessment
Perform a comprehensive assessment of your city’s current state, including resource consumption patterns, environmental impacts, infrastructure capacity, and socioeconomic factors. This baseline data will serve as a reference point for measuring progress and identifying areas for improvement.
3. Identify data sources and establish data collection mechanisms
Identify relevant data sources, including sensor networks, citizen feedback platforms, and existing databases. Establish robust data collection mechanisms to ensure the quality, consistency, and reliability of data.
4. Develop a data management and analytics strategy
Define a clear strategy for data management, storage, and analysis. Establish data governance policies, define roles and responsibilities, and identify the necessary analytical tools and techniques.
5. Engage stakeholders and foster collaboration
including citizens, businesses, academia, and government agencies, in the development and implementation of the data-driven sustainability plan. Collaboration and co-creation foster buy-in, trust, and sustainable solutions tailored to local contexts.
6. Implement pilot projects and measure impact
Start with pilot projects focused on specific sustainability challenges or domains, such as energy efficiency, waste management, or transportation. Measure the impact of these initiatives using data-driven metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
7. Scale and integrate successful initiatives
Based on the success of pilot projects, scale and integrate successful initiatives into a comprehensive data-driven sustainability plan. Ensure interoperability and integration across different urban domains for a holistic approach.
8. Continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation
Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the data-driven sustainability plan. Use feedback loops to refine strategies, incorporate new data sources, and adapt to changing circumstances and emerging challenges.
9. Foster capacity building and knowledge sharing
Invest in capacity building and knowledge sharing initiatives to empower stakeholders with the necessary skills and expertise to leverage data and analytics for sustainable decision-making.
10. Promote transparency and accountability
Ensure transparency in data collection, analysis, and decision-making processes. Establish mechanisms for public accountability, enabling citizens to scrutinize and provide feedback on data-driven sustainability initiatives.
By following these steps, cities can develop a comprehensive and tailored data-driven sustainability plan that leverages the power of data and analytics to drive urban resilience and sustainable development.
Best practices for measuring and monitoring sustainability metrics
Measuring and monitoring sustainability metrics is essential for tracking progress and making informed decisions. To do this effectively, cities should start by establishing clear and measurable indicators that align with their sustainability goals—these should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Utilizing standardized frameworks, like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards, helps ensure consistency and credibility in reporting.
Integrating data from various sources, such as sensor networks and citizen feedback, provides a comprehensive view of sustainability performance. Developing user-friendly dashboards and visualizations makes it easier to present this data clearly, facilitating better decision-making and stakeholder engagement. Setting baseline values for metrics allows cities to measure progress over time, while defining target values helps them strive toward specific sustainability goals. Regular audits and assessments of data accuracy are crucial, and involving third-party auditors can enhance transparency.
Engaging stakeholders – citizens, businesses, and community organizations – in the measurement process fosters collaboration and accountability. Continuous improvement is key, so cities should regularly review and adapt their metrics and methodologies to meet emerging challenges. Participating in benchmarking initiatives and collaborating with other organizations can also help cities learn from best practices. Finally, integrating sustainability metrics into decision-making processes at all levels ensures that these metrics inform urban planning and resource allocation.
By following these best practices, cities can effectively monitor their sustainability efforts, enabling data-driven decisions and promoting continuous improvement toward urban resilience and sustainable development.
The future of data-driven sustainability is now
As we look to the future, it is evident that data-driven sustainability is not merely an option but a necessity for cities aiming to achieve urban resilience and sustainable development. The convergence of technological advancements – such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and artificial intelligence – has unlocked new avenues for data-driven decision-making and innovative solutions.
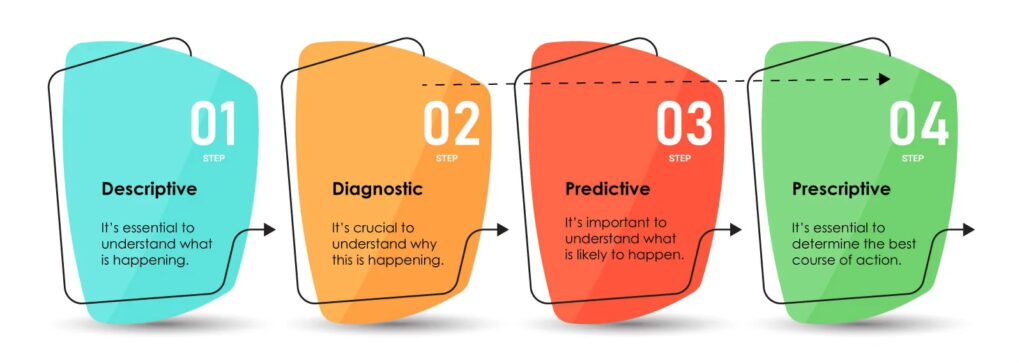
In this evolving landscape, the future of data-driven sustainability will be marked by enhanced integration and interoperability of data systems. This will facilitate a holistic and interconnected approach to addressing urban challenges. To effectively navigate this complexity, it is essential to consider various analytical dimensions:
- Descriptive: Understanding what is happening in our urban environments.
- Diagnostic: Analyzing why these changes are occurring.
- Predictive: Anticipating what is likely to happen in the future.
- Prescriptive: Determining the best course of action to take.
Data-Driven Sustainability: Unlocking the full potential of your data
In summary, data-driven sustainability is the key to developing smart, resilient cities capable of proactively addressing the challenges of tomorrow. By leveraging data effectively, urban areas can foster sustainable growth and enhance the quality of life for their residents.
Literature
- Leveraging transboundary interactions for urban resilience and sustainability: https://www.the-innovation.org/article/doi/10.59717/j.xinn-geo.2024.100084
- Data-driven smart sustainable cities of the future: urban computing and intelligence for strategic, short-term, and joined-up planning: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s43762-021-00008-9
- Enhancing Urban Resilience: Smart City Data Analyses, Forecasts, and Digital Twin Techniques at the Neighborhood Level: https://www.mdpi.com/1999-5903/16/2/47
- Environmentally sustainable smart cities and their converging AI, IoT, and big data technologies and solutions: an integrated approach to an extensive literature review: https://energyinformatics.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s42162-023-00259-2
- Big Data-Driven Urban Management: Potential for Urban Sustainability: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/11/5/680



